Трубный насос API
- 40-летний опыт проектирования и изготовления скважинных насосов.
- Участвовал в разработке национального стандарта на скважинный насос.
- 20-летний опыт производства насосов для НКТ API11AX.
- Три ведущих китайских производителя насосов для НКТ API 11AX
Ваш премьер
API 11AX Штанговый насос Производители и поставщики
Различные типы насосов для НКТ
Sanjack может производить различные типы насосов для труб, такие как THD, THM, THC.
Строгий контроль качества
Национальные лаборатории проводят инспекцию сырья, инспекцию производства и общие испытания герметичности.
Современное производственное оборудование
Современное производственное оборудование
Сопротивление ржавчине
Sanjack использует множество антикоррозионных технологий, таких как борирование, азотирование, хромирование и покрытие вольфрамом.
- Годовой объем производства: 15000 комплектов
- Коррозионная стойкость и износостойкость
- Фиксированный клапан не подлежит спасению
- Скважина с низкой глубиной и высокой производительностью
Цех штанговых насосов Sanjack был основан в 1964 году и имеет более чем 50-летнюю историю. У нас есть богатый опыт производства и сильные способности в исследованиях и разработках. Наша продукция включает различные серии насосов для НКТ, штанговых насосов и специальных штанговых насосов. Мы получили 32 национальных патента на технологию забойного насоса. Эти продукты экспортируются в SHELL, CHEVRON, GE, SCHLUMBERGER, NOV, JOHN CRANE, CAMERON, KBM и др. Наша годовая производственная мощность составляет 15000 комплектов.
Send us your requirement, Let Sanjack support you
API 11AX Tubing Pump: The Complete Guide for Importers and Buyers
API 11AX Tubing pumps are said to be positive displacement pumps used to transfer a wide variety of fluids in oil wells.
These pumps work by holding a fixed volume of liquid that needs to be pumped and then forcing it from the inlet end to the discharge end.
Some types of positive displacement pumps use cavities that expand at the suction end and contract at the discharge end, while the liquid volume in the cavity remains constant.
API tubing pumps are categorized under various heavy-duty displacement pumps that discharge a large volume of fluids to high head.
The size of the tubing determines the maximum production that the pump produces.
However, there are some differences between tubing pumps and insert pumps.
One of these is that API tubing pumps have a larger plunger diameter that allows the pump to have a more significant fluid load than insert pumps.
Therefore, it is worth noting that the depth at which an API tubing pump can run is quite limited, depending on the rod string and the size of the pumping equipment on the surface.
Accordingly, the pump barrel works as a section of the tubing pump, while the plunger and the traveling valve run in the well alongside sucker rods.
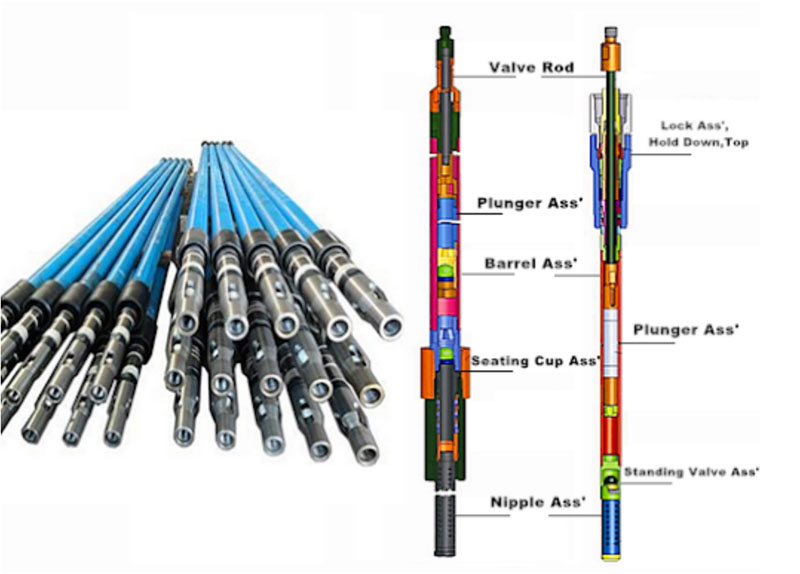
API tubing pumps basics
API tubing pumps are high volume, heavy-duty pumps used in oil wells. The production of oil and gas depends significantly on the size of the tubing pump.
Accordingly, we have discussed that the depth that a tubing pump can run depends on the rod string and the size of the surface pumping apparatus.
But what are these types of equipment? Do not worry; we are here to let you know more about them to make an informed buying decision the next time you want to purchase an API tubing pump.
The first thing you need to understand is that a standing valve can be categorized under either;
- Fixed
- Retrievable(Fishable)
The fixed type has its components attached below the pump’s barrel and used as a section of the stubbing string. A larger valve can be installed in fixed types compared to retrievable(fishiable) types.
However, the tubing must be pulled when a need to repair it arises. Additionally, the entire tubing string must be pulled to repair the barrel on an API tubing pump.
On the other hand, the retrievable(fishiable) type standing valve is designed to rest in a cup-like or mechanical-type seating nipple below the pump barrel. This valve can be removed using a sucker string and valve puller attached at the lower end of the plunger permanently.
API tubing pump components
Tubing pumps are downhole mechanical lift systems used to transfer fluids in oil wells. These pumps usually have the following five key components:
- Barrel Tube
- Hold-down Seal Assembly
- Plunger
- Standing Valve
- Traveling Valve
Barrel tube
A barrel tube is a section of the pump where the fluid flows from the formation. The pump barrel can either be a section of the tubing or a different component altogether, depending on the design of the tubing pump. Barrels can be made different using various types of metal, metal thickness, and way the barrel houses the plunger.

In most cases, manufacturers make pump barrel in one of the following three thickness sizes:
- heavy wall
- thin wall
The material used to make the barrel tube can vary in type and grade of the metal. You will find API tubing pump manufacturers using brass, carbon steel, Monel, or stainless steel in most cases. These materials can be treated to prevent chemicals and corrosion, depending on the manufacturers’ preferences. The treatment also helps to harden the metal to give barrels additional strength.
Before installing the barrel, it’s machined to ensure the utilization of correct thread designs and clearances, depending on the plunger-type. A liner is sometimes used, mostly when the barrel is made to accommodate extra layering.
Hold-down seal assembly
A hold-down seal assembly is used to create a seal between the tubing and the pump. One of the three types of hold-down assemblies is applied; one cup type and two mechanical options. Each seal assembly has to be installed accurately to utilize an appropriate seating nipple in the tubing string.
For cup-type assemblies, you will find that they use one of two seating nipple lengths. The shorter version offers one seating area while the longer one provides the ability to be reversed, which allows it to turn in the tubing to form a new seating area when other areas are damaged.
Both cup and mechanical styles offer accurate installation. However, operators should go for mechanical hold-down options when the bottom hole temperature is 250 degrees Fahrenheit and above.
Plunger
The plunger is specifically designed to aid the transfer of liquid from the pump’s base to the top of the pump. The motion of fluids in the plunger can either be controlled by the barrel’s movement around the plunger or the movement of the plunger within the barrel.
The plunger can either be metallic or nonmetallic, and each type is available in a large variety of metal arrangements. The arrangements are mostly designed to allow similar treatment used on the barrel.
The space between the metallic plunger and the barrel has to be extremely accurate to offer a successful tubing pump assembly. Therefore, the spaces are often corrected after the tubing pump is installed in the hole.
This is generally done as a system normalization to the temperature of the pump and the bottom hole. The plunger and barrel are treated to withstand corrosion from hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide gases in the wellbores.
The use of a grooved or non-grooved plunger depends on the condition of the well.
Nonmetallic plungers (soft-pack plungers) are designed in either cup or ring types.
Ring design can also be called composition ring, regular flexite, soft-packed, wide flexite, among other terms.
Nonmetallic cup assembly and composition are chosen depending on the well condition, such as abrasiveness, corrosive fluid properties, fluid temperature, fluid gravity, and lubrication type.

Standing Valve
A standing valve found at the base of the tubing pump is a one-way valve that allows fluids to flow from the pump’s formation to the barrel. The standing valve is made up of a ball resting on a small-lipped seat. Ball and seat assembly are located within a valve cage with a ball on top and positioned in the wellbore.
API tubing pumps are designed to use pressure from above the ball to keep it intact in the seat and prevent the fluid’s flow back past the valve. This is done explicitly because the pressure from below can unseat the ball and leak fluid past the valve. The ball and seat are installed and sealed as a unit.
The ball and seat should always be kept as a unit with each seat having two options of sizes of balls. These options are the standard API size and a smaller version that allows violent fluids and debris to move between the ball and valve guide. Double valves may be used for some applications to solve specific issues.
Traveling Valve
A traveling valve is found on the pump’s height. This is also a one-way valve, and it allows fluids to flow out of the barrel and prevents backflows.
The traveling valve and standing valve are separate components of a tubing pump.
However, the two valves can be of the same composition and size, which allows them to be used interchangeably. Accordingly, the construction and operation of the traveling valve and standing valve are similar.

Different ranges of API tubing pumps
API tubing pumps are available in a large variety of lengths and materials to offer solutions to different downhole challenges.
This is mainly why you need to understand different types of API tubing pumps if you want to buy one suitable for your oil well applications. The following are some of the tubing pumps ranges you can consider:
- TH Pumps
SanJack Petro designs tubing pumps that can handle more rugged oil well conditions such as high pressures, volumes, and depth. When using the TH tubing pumps, you can expect maximum production, depending on the tubing size.
Accordingly, TH tubing pumps are suitable for deep horizontal oil well applications because they do not have a seating mechanism.
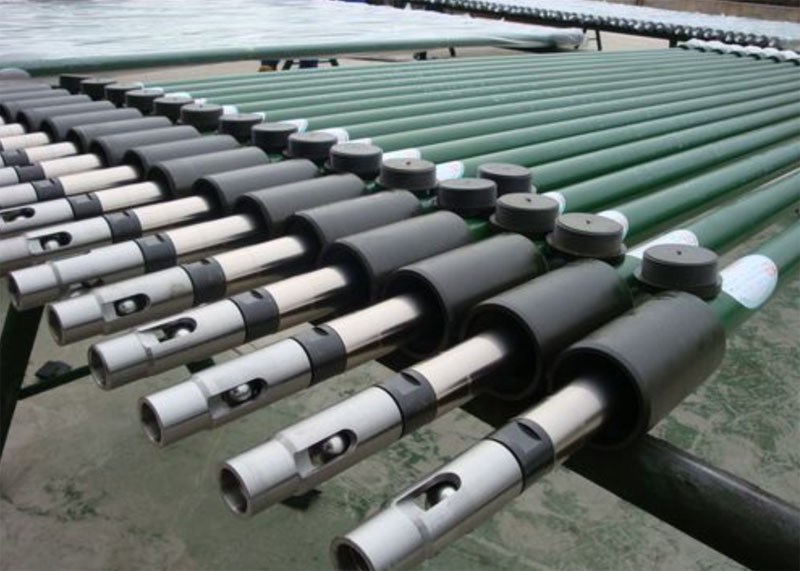

API Designation for TH pumps include:
- 25-175-TH
- 25-225-TH
- 30-275-TH
- 40-325-TH
- 40-375-TH
-
TW Pumps
TW tubing pumps are designed for deeper wells that produce sand, scale, paraffin, and high gas levels. These pumps have heavy wall barrels and are recommended for deeper, deviated oil wells. The API designation for TW tubing pumps include:
- 20-125-TW
- 20-150-TW
- 25-200-TW
-
OTP Pumps
Oversized Tubing Pumps, abbreviated as OTP pumps, are designed for high-volume wellbore applications that require a larger pump bore than the tubing ID. These pumps are made to utilize impact-resistant cages that offer superior durability and chemical resistance compared to conventional hard-lined cages. The API designation for OTP pumps include:
- 25-175-OTP
- 25-225-OTP
- 30-275-OTP
- 40-325-OTP
- 40-375-OTP
Tubing pump vs. insert pumps
The type of mechanical lift system you use in oil wells does not matter because it all comes down to some sorts of pumping configuration to transfer hydrocarbons from inside the wellbore to the surface. While there is a wide variety of styles to choose from, every downhole pump utilizes similar essential components.
The distinction between downhole pumps is often found in their functionality and how various components are put together. If you intend to buy any downhole pump, you need to understand the similarities and differences between inserts pups and tubing pumps.
Downhole pump designs
Three types of pumps and one tubing pumps are often used in four basic styles of downhole pumps. However, the two broad types are insert pumps and tubing pumps.
-
Insert Pumps
In oil and gas production, insert pumps are already constructed as complete and functional pumps placed in the tubing string. Insert pumps have one of either stationary or moving barrel. The pump is often anchored to either top or bottom. Because of these possibilities, insert pumps are made in three different designs, namely;
- Stationary Barrel, Bottom Anchor
- Stationary Barrel, Top Anchor
- Traveling Barrel, Bottom Anchor
-
Tubing Pumps
The most notable difference between an insert pump and a tubing pump is that a tubing pump is placed down the hole as part of the tubing string with a standing valve and a traveling valve running on the rod string. The rods turn and discharge the standing valve once it drops to the base of the hole.
The pump starts pumping again once the rods are repositioned some inches higher. Standing valves are often attached or re-attached in tubing pumps for re-running, pulling, and servicing rods.
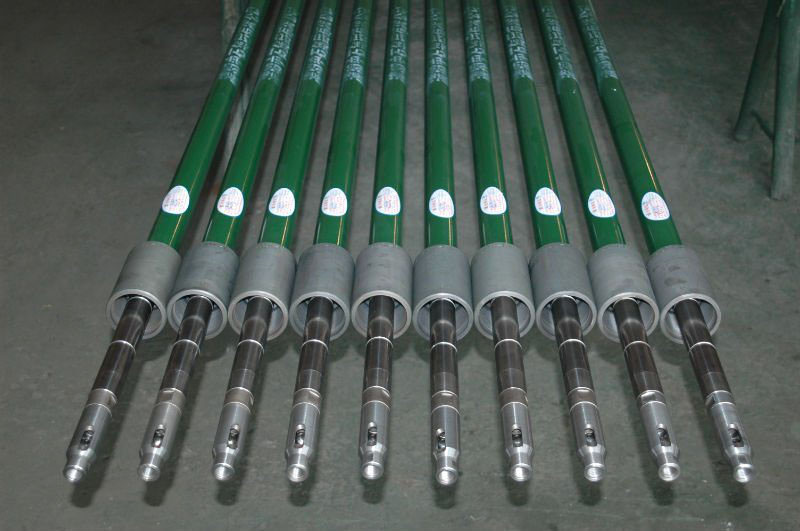

The bottom line
One advantage of a tubing pump lies in its ability to pump larger volumes in waterflood plans.
However, many other advantages make API tubing pumps the most preferred in downhole applications. On the flip side, a big disadvantage of the API tubing pump is that it requires you to remove the tubing string for pump barrel maintenance and servicing.
Another disadvantage lies in the fact that API tubing pumps have rod strings with a higher fluid load. This makes the weight of the load to stretch the rod, leading to a bottom hole stroke loss.
- Alternative Pump Types
Like any other device, downhole pumps come in a wider variety of designs and sizes. While some of these are discussed in this guide, others remain unique and designed to meet specific oil and gas production requirements.
Therefore, pump manufacturers are supposed to offer comprehensive assistance when planning your pump installation design, especially when working on special conditions.
Always ask for an expert opinion before buying an API tubing pump or any other wellbore equipment. At SanJack Petro, we analyze different well conditions and design our tubing pumps to meet even the most demanding requirements.
Related:






